The National Energy Policy Council has approved the Master Plan for Thailand Smart Grid Development (2015-2036), which is expected to involve a total investment of about Bt200 billion for the 20-year period. Twarath said between three and five pilot projects, two of them in Mae Hong Son province, would be implemented during the first five years by the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (Egat), the Provincial Electricity Authority (PEA), and the Metropolitan Electricity Authority (MEA). Egat has chosen Muang district of Mae Hong Son to trial its first smart-grid project, while PEA has selected Mae Sariang in the same province and Betong in Yala.
The MEA, meanwhile, is eyeing some industrial estates in its coverage area, which comprises Bangkok, Nonthaburi and Samut Prakan, to test a smart grid. These pioneer smart-grid projects are expected to reduce peak power demand by a total of 350 megawatts. Private companies will be allowed to invest in smart-grid projects in the future, he said. The smart grids’ objectives are to enhance energy security, improve productivity and services through information and communication technology, and move towards a more sustainable, low-carbon economy, with greater use of renewable resources.
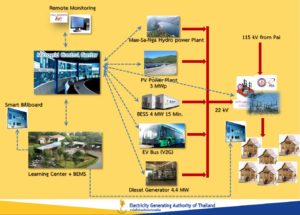
The system reliability is a main factor that affects on the growth of business in Mae Hong Son Province, which is located in the Northern region of Thailand. Mae Hong Son Province is far as deep valley hemmed in by the high mountain ranges of the Shan Hills. Since it is the mountainous province in the Northern part, the electricity is hardly supplied through the transmission line. There is no transmission line of the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT) linked from the main grid to Mae Hong Son Province due to the limitation of line routes passing prohibited areas, such as watershed area class 1 A and national park. The power is currently delivered through the distribution line of Provincial Electricity Authority (PEA) by receiving the electric power from EGAT at the Mae Tang Substation of EGAT through 115 kV and 22 kV distribution lines. Moreover, the demand consumption is fulfilled by very small power plants (VSPP) in Mae Hong Son Province. In case that the power demand of Mae Hong Son Province during the hot season is increased very much, the dispatching on diesel generators is required with high fuel cost. Sometimes, it also effects on the system reliability and power quality in Mae Hong Son Province
EGAT is undertaking the study to develop the national pilot project with the collaboration of related organizations to improve the system reliability for Mae Hong Son Province. From the energy supply aspect, Mae Hong Son Province has several basic factors to enable the renewable energy generation, that is, high potential renewable energy including solar, hydro, biomass, and biogases. However, most renewable energy resources are intermittent, the smart grid technologies such as: energy storage and demand response shall be applied to handle the uncertainty of the power supply. The generation capacity in Mae Hong Son Province shall meet with the power demand in the province with sustainable and green power supply. From the operation point of view, the system reliability can be improved with the automatic control and operation, for example, self monitoring and self healing. The network can be automatically adapted and isolated when faults occur in the electrical system. With this concept, the power grid shall be smarter.