I.Background
Taoyuan was once known as the “Kingdom of Herbs and Flowers” of Chinese Taipei and the “Homeland of Rice” in northern Chinese Taipei. Not only had it over ten thousands of ponds for the purpose of irrigation, but it also was the biggest granary in northern Chinese Taipei. Following the change of times, Taoyuan has already become the city of technology and intelligence; and among all cities and counties of the country, is the one that is the closest to the world nowadays. Challenged by environmental degradation and resource exhaustion of mother earth, we are forced to think about how to maintain green sustainability and resource circulation economically. On the other hand, the country’s poor self-sufficiency and food safety issues also forced us to think how to face unprecedented changes and reminded us the importance of “agriculture” in regard to our future survival. These are the responsibilities that Taoyuan shall not run away from.
Over the last hundred years, agriculture has been playing an important role in the development of Chinese Taipei’s economy. Therefore, we are willing to become the leader to rethink our position and, by adopting smart and low-carbon agriculture, show everybody the characteristics of local agriculture, the possibilities for agricultural technology and the competence of Taoyuan’s unique agriculture. It is our objectives not only to redefine our agricultural products, think about the relationship between human and the nature and then create a higher value for life, but also to find the opportunities for agricultural transformation and to create more opportunities for agricultural development in order to minimize the development gap between towns and the cities. In this way, we will be able to welcome a better future.
II.Changes
In the past, Taoyuan’s traditional agriculture heavily relies on human force, materials and equipment. Although the City succeeded in creating abundant and diverse agricultural products, but it also consumed energy. Today, not only is Chinese Taipei’s agriculture challenged by international market competitions, but also the age of global climate disorder and high energy price has arrived. Therefore, adjustments with modern tools are required for agricultural sustainability.
In recent years, Taoyuan has an outstanding performance in developing itself into a smart city. On February 8, 2018, the international organization “Intelligent Community Forum” (ICF) announced the candidates of the TOP 7 of 2018 in Hunter College, the City University of New York, and for the third time in the history (in 2013 and 2017), Taoyuan received the honor thereof.
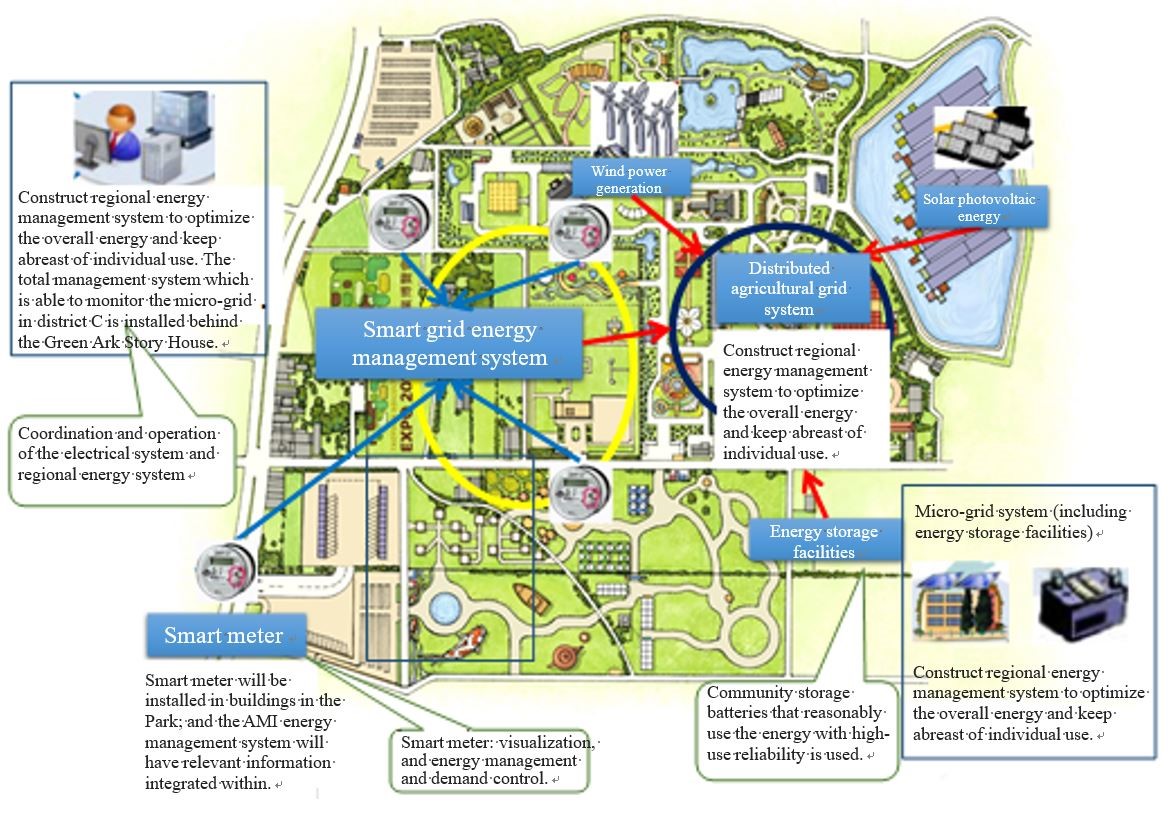
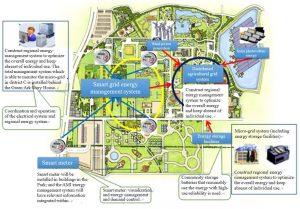
While developing cloud intelligence and technology applications, the City also thinks about the interdependence between the “human, land and natural ecology”. The country’s first distributed agricultural electric grid is therefore invented to conduct relevant planning and to have this concept applied in the City. It is expected that, by connecting to smart technology, looking for opportunities for agricultural transformation and adopting renewable energy, Chinese Taipei will be able to balance its production, life and ecology and further become a low-carbon emission and sustainable city.
III.Demonstrative Implementations
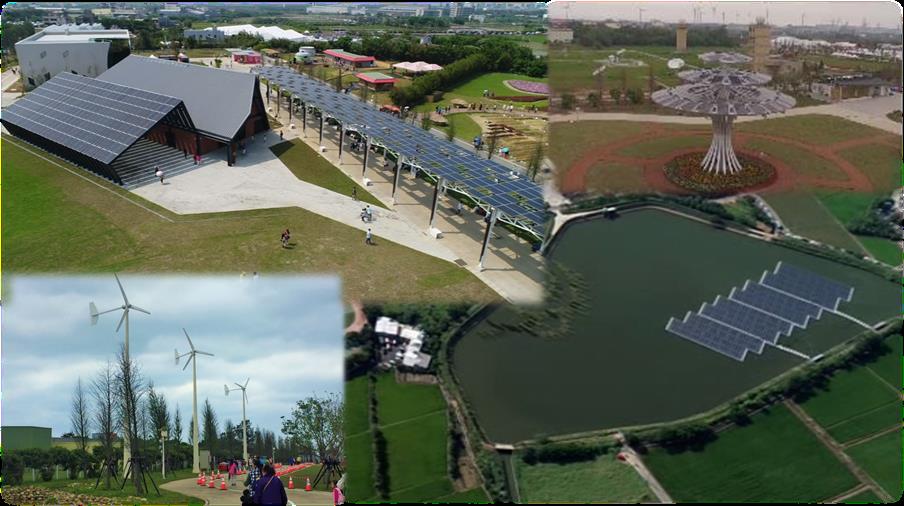
The country’s first distributed agricultural electric grid is demonstrated in the agricultural village, Xinwu. Sized 30 hectares, the demonstration is presented in forms of “Taoyuan Agriculture Expo” (TAE) to let more people know about the planning and design of agricultural electric grid system, including the adoption and installation of renewable energy facilities, control of agricultural smart grid system and energy storage equipment.
1.Objective: An expo with no power consumption
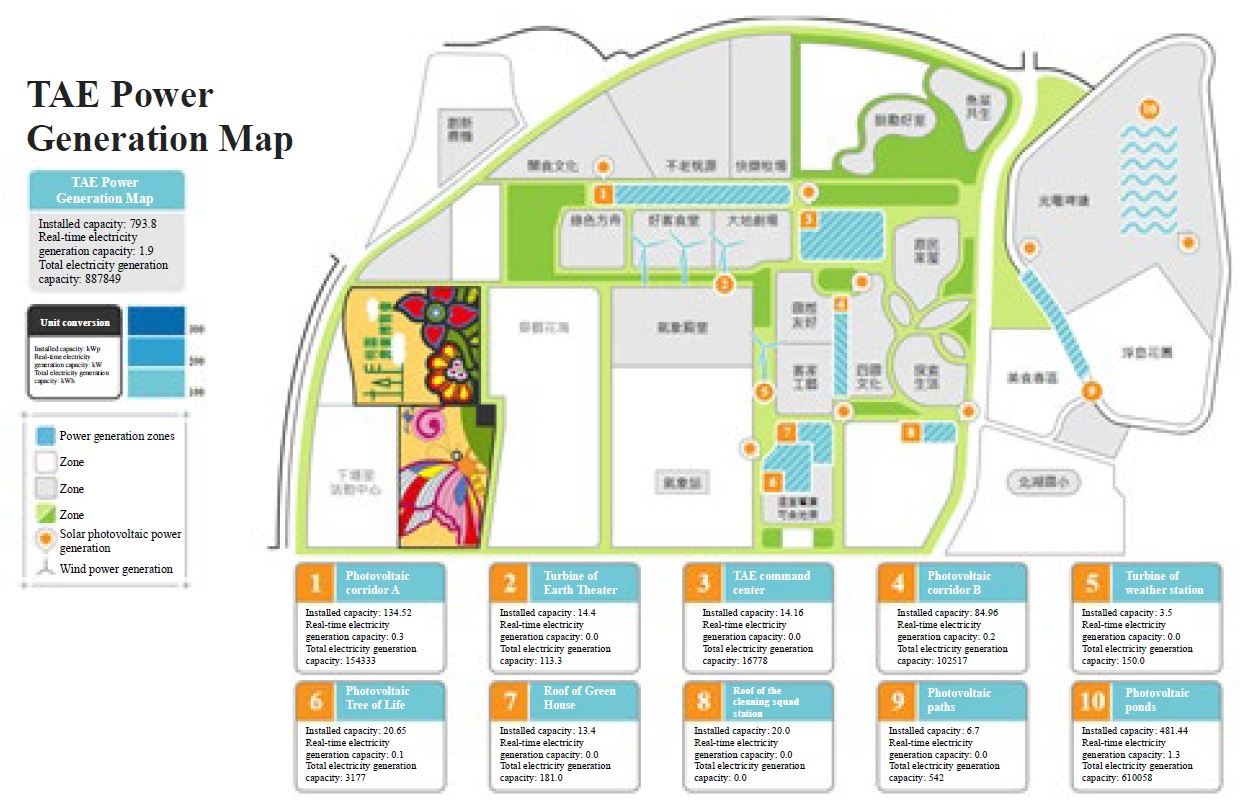
This time, when promoting the development of green energy policies, Taoyuan City has diversified the use of existing space under the consideration of high population and insufficient land of use. For example, it has combined the solar photovoltaic systems with the pond culture in 2016, and selected ponds 12 to 14, which are located in the front side of the TAE base, to install Chinese Taipei’s first floating island photovoltaic system.
Apart from photovoltaic ponds, other types of solar photovoltaic and turbine systems were also installed at the TAE site. For example, the TAE park totally produced 127,970kWh of electricity (as shown in Table 1), which can be seen from the monitoring system during the period of this event (April 4 to May 13). This enormous amount of electricity produced by the Park, which is enough to supply 427 families for a month, therefore guaranteed the supply of electricity required thereby. Apart from the distributed electric grid based design, smart meter and energy storage system were also adopted for resource allocation and management of the site, making TAE “an expo of no power consumption” for the first time in Chinese Taipei during 40 days of the expo.
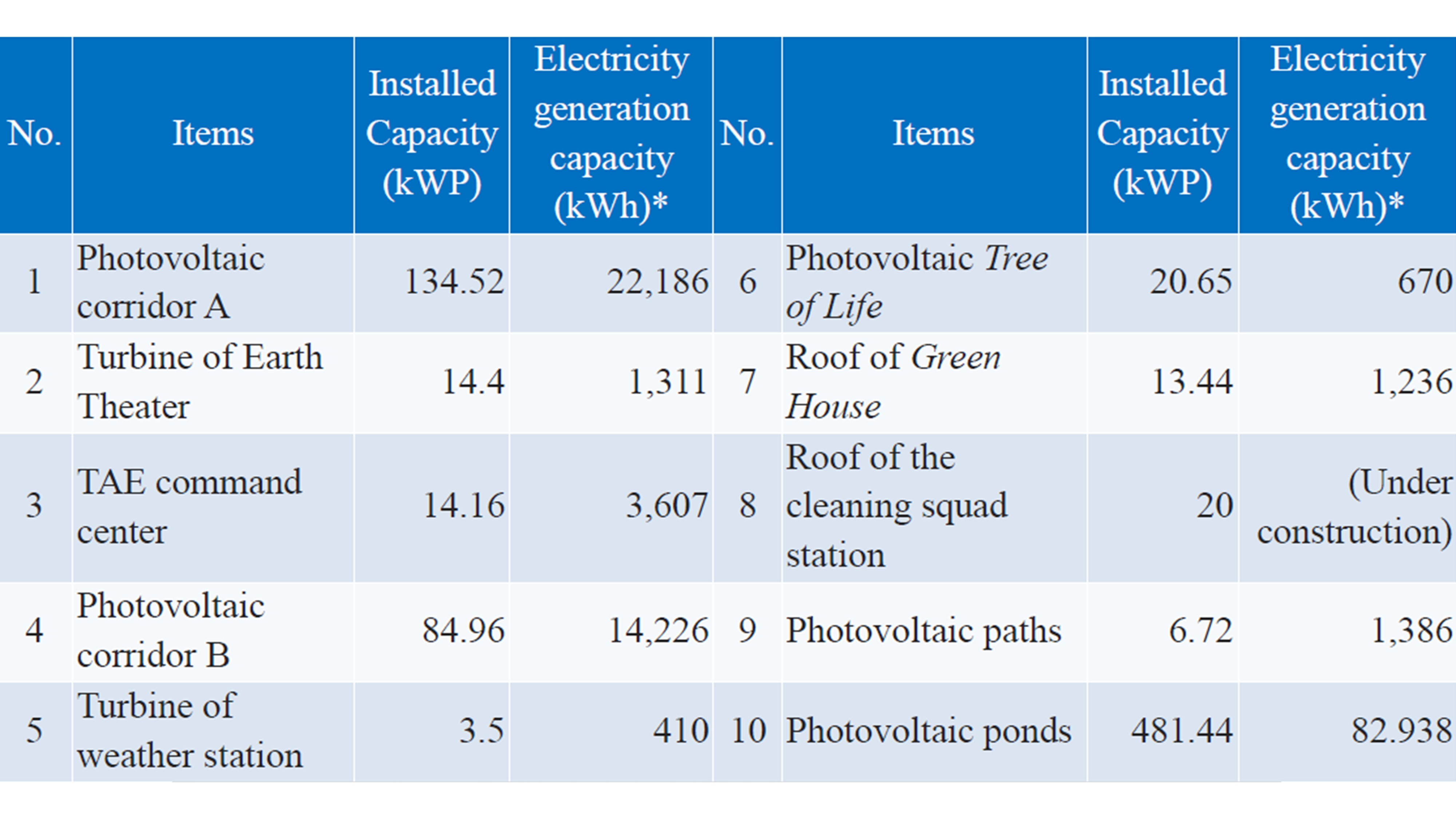
Table 1. The renewable energy installed capacity of Taoyuan Agriculture Expo (TAE)
Figure 1. Installed renewable energy
2.Installation and demonstration of the agricultural smart grid system
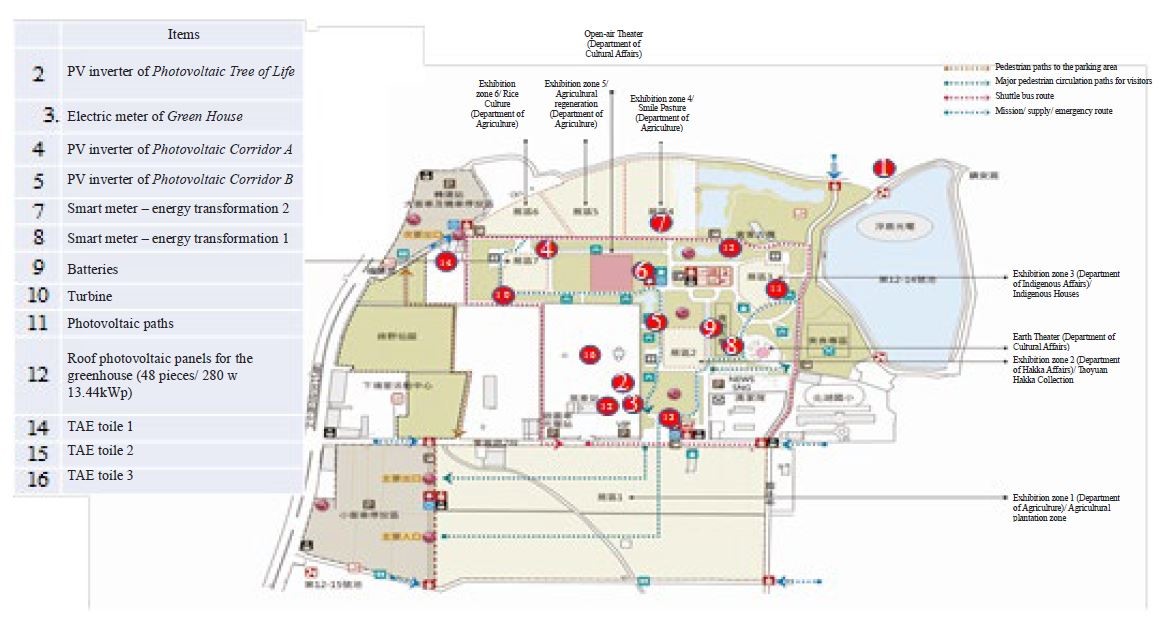
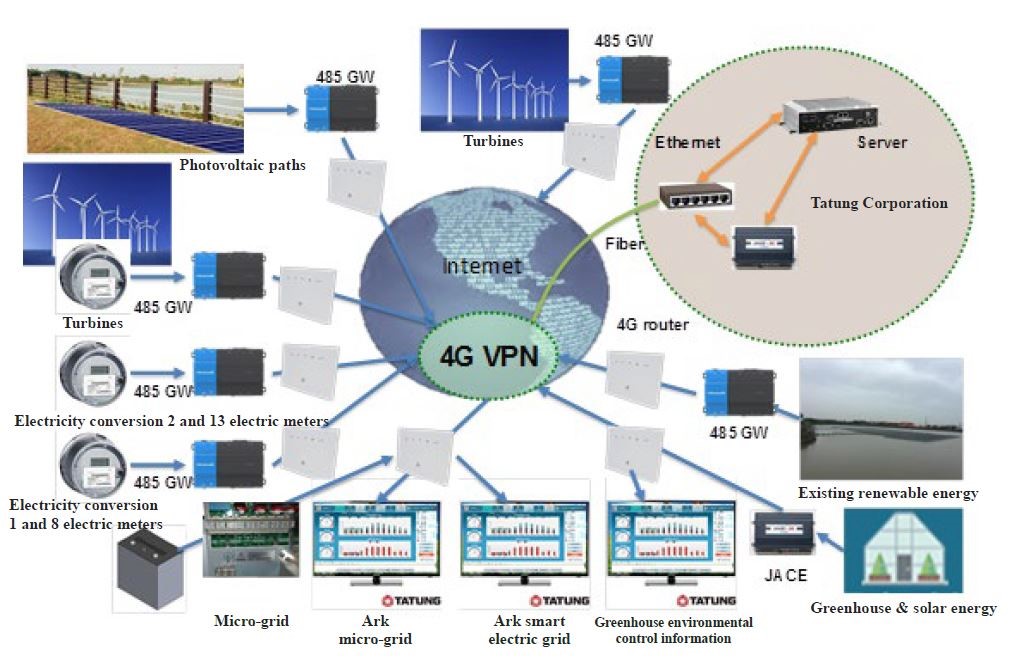
Integrate and arrange 10 renewable energy installation facilities, smart meters and energy storage batteries; and establish over 20 smart grids and have them integrated in the agricultural smart grid system with the 4G network for the monitoring and demonstrations.
Figure 2. Framework of agricultural smart grid system
Figure 3. Installation of electricity monitoring facilities at TAE
Figure 4. The smart grid monitoring framework of TAE
(1)System demonstration:
The information of the agricultural smart grid system was presented in 5 pictures, including:
Figure 5. Taoyuan Agriculture EXPO Smart Grid System
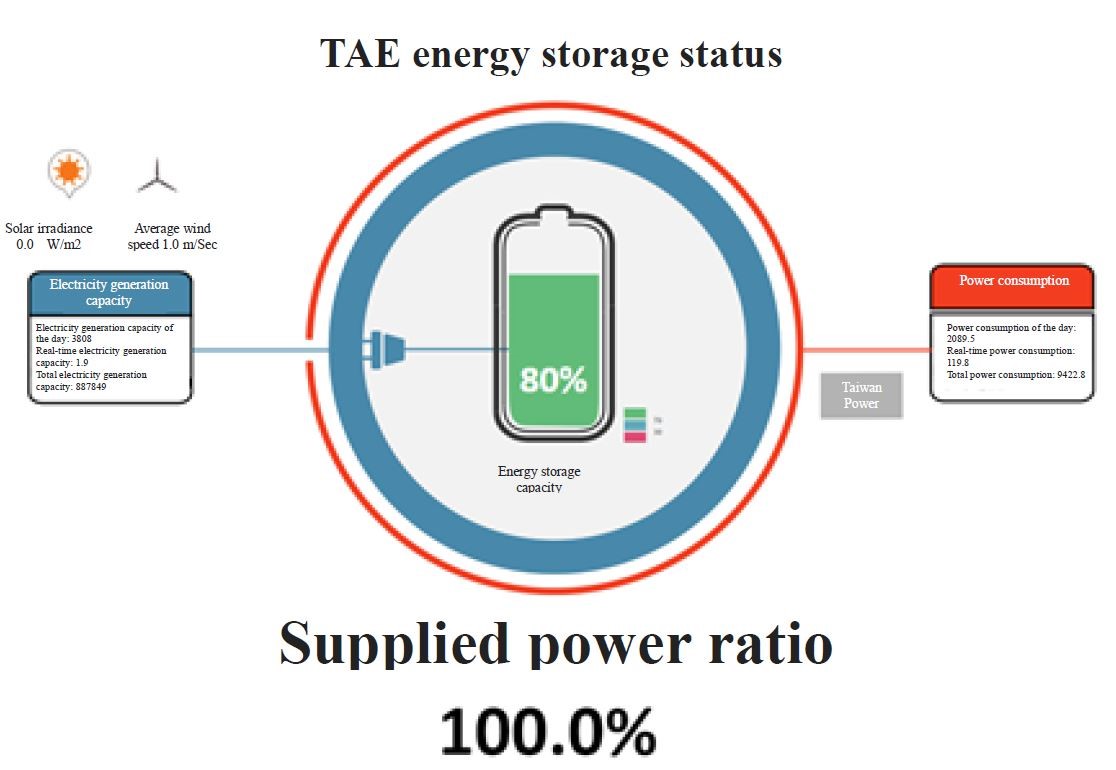
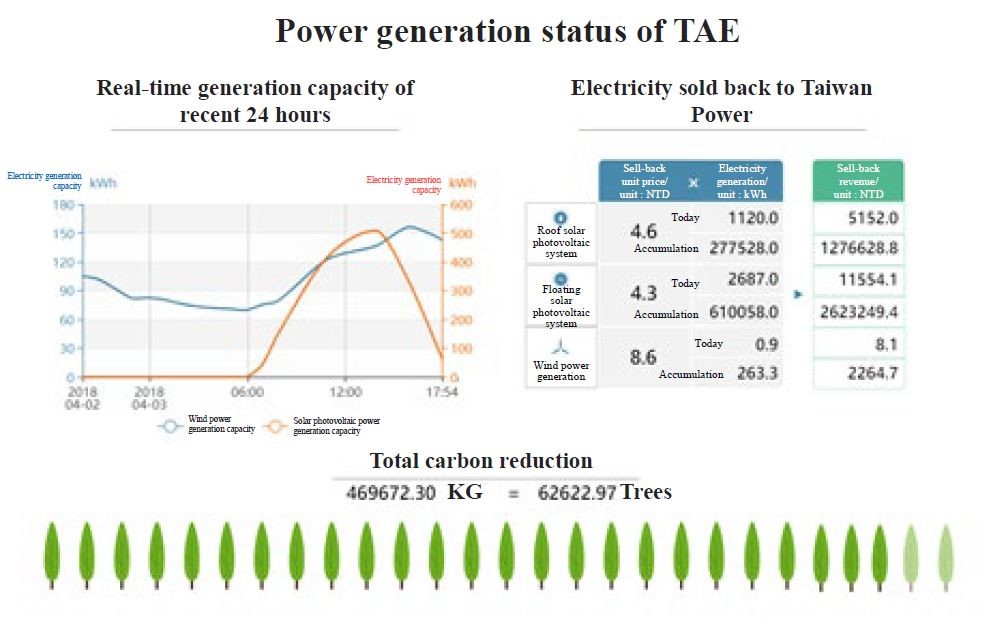
(2)Energy storage:
The total renewable electricity generation and total power consumption of the TAE Park are displayed. When the renewable electricity generation capacity is higher than the power consumption, the supplied power ratio of renewable energy is 100%; when it is lower than 100, it implies that the park is using the electricity of Taiwan Power Company. The energy storage strategy, on the other hand, is to recharge the batteries during night time when the wind power generation takes place. The stored energy was then used for the TAE Park when the power consumption reached peak at noon.
Figure 6. Energy storage display
(C)Electricity generation map:
The map shows the electricity generated from solar photovoltaic and wind power; and is presented in three class intervals: the higher level the generated electricity is the darker color it will be.
Figure 7. Electricity generation map
(D)Power generation status:
The generated electricity from renewable resources is converted to “money” and “trees” to facilitate visitors’ understanding thereto.
Figure 8. Power generation status display
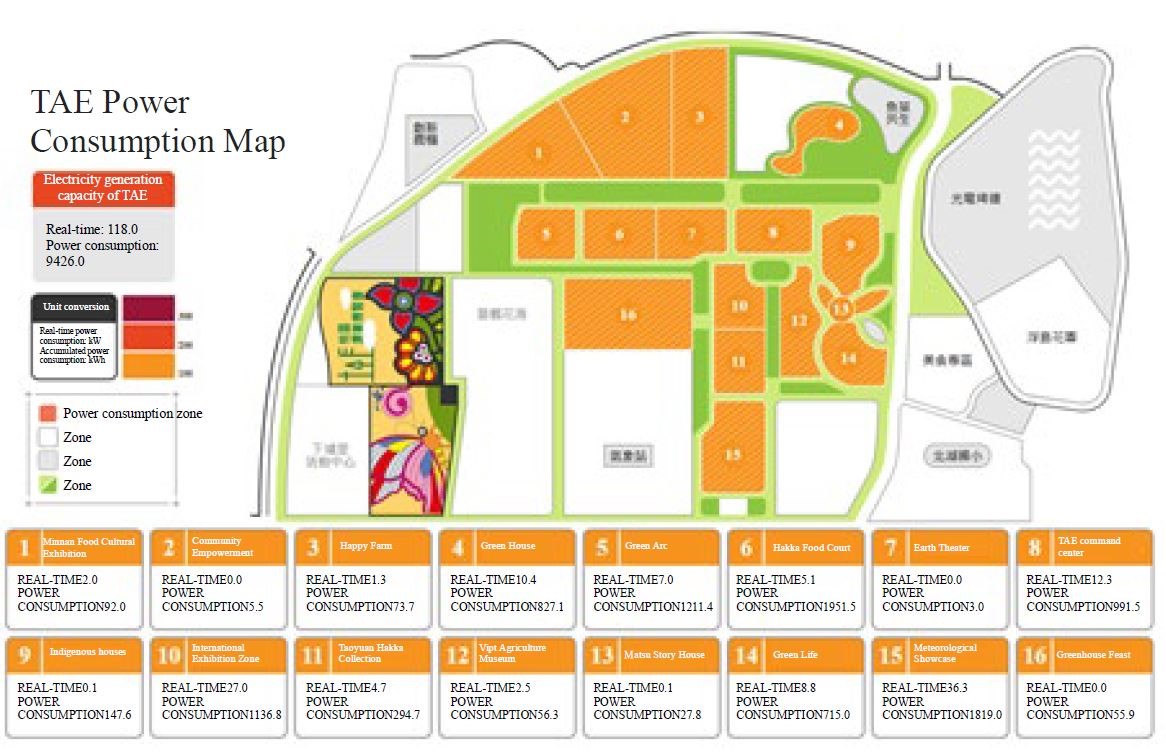
(E)Power consumption map:
The power consumption of 16 TAE zones is herein presented in three class intervals. The more electricity consumed the darker color it will be. Where the power consumption is a negative value, it implies that the region’s generation of renewable energy is higher than its consumed electricity and that the rest electricity will be used to support other zones.
Figure 9. Power consumption map
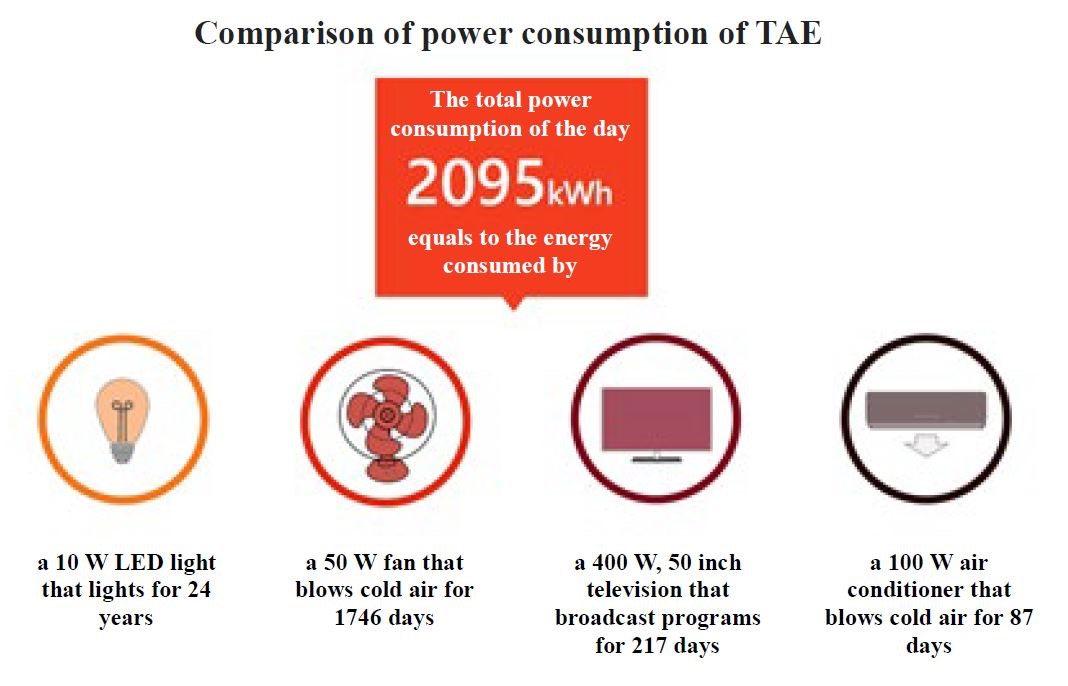
(F)Comparison of power consumption:
The power consumption is presented in the usage of four home appliances (number of days or years) to facilitate visitors’ understanding thereto.
Figure 10. Comparison of power consumption
3.Energy storage technology combination
Energy storage technology plays a very important role in stabilizing the grid and improving the application of renewable energy. This time, combined with the energy storage system, the output of renewable energy can be more stable, and balance the function of power consumption, stable power supply, frequency, and further improve the efficiency of the entire power system and the economic benefits of power generation.
For the energy storage system parallel grid and regional decentralized energy system, the integration of the power management platform effectively operates the distributed energy in the control area, and with the energy storage management system to improve the quality of the power system. In this way, it can be expected to effectively expand the distributed energy and Renewable energy supply to approach the goal of the government’s promotion of low-carbon communities.
4.The agricultural smart grid series system
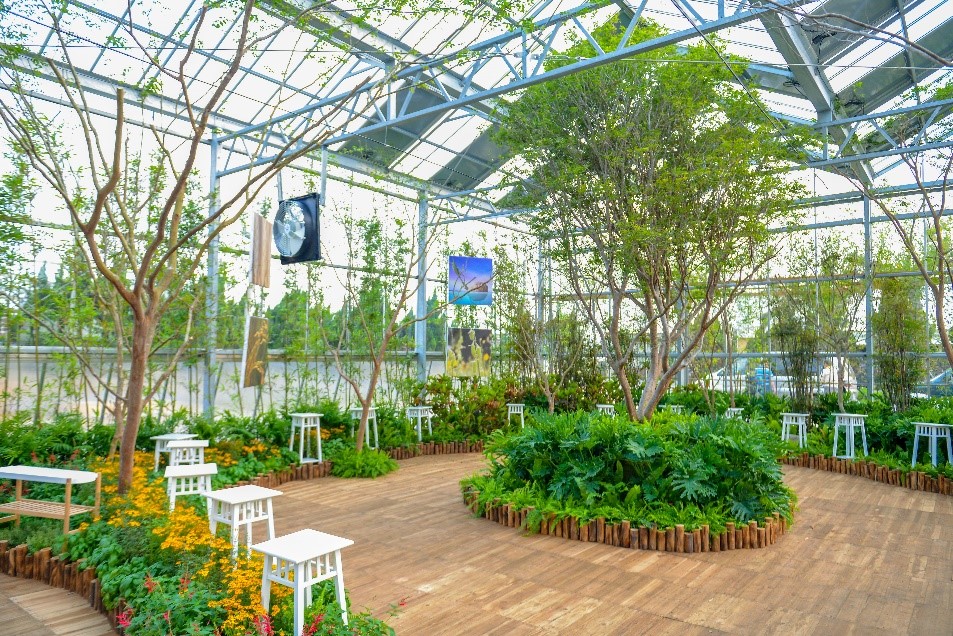
(A)Green energy smart glass green house
The agricultural smart grid is connected to the “green energy smart glass green house” to adopt solar photovoltaic, cloud smart monitoring and automated control systems to optimize the electricity usage of the Park. Besides, the green house system that controls the humidity and temperature according to the weather broadcast also facilitate the management of farm production relevant affairs.
Figure 11. A corner of the green energy smart glass green-house
5.Applications and demonstrations of other additional energy technology
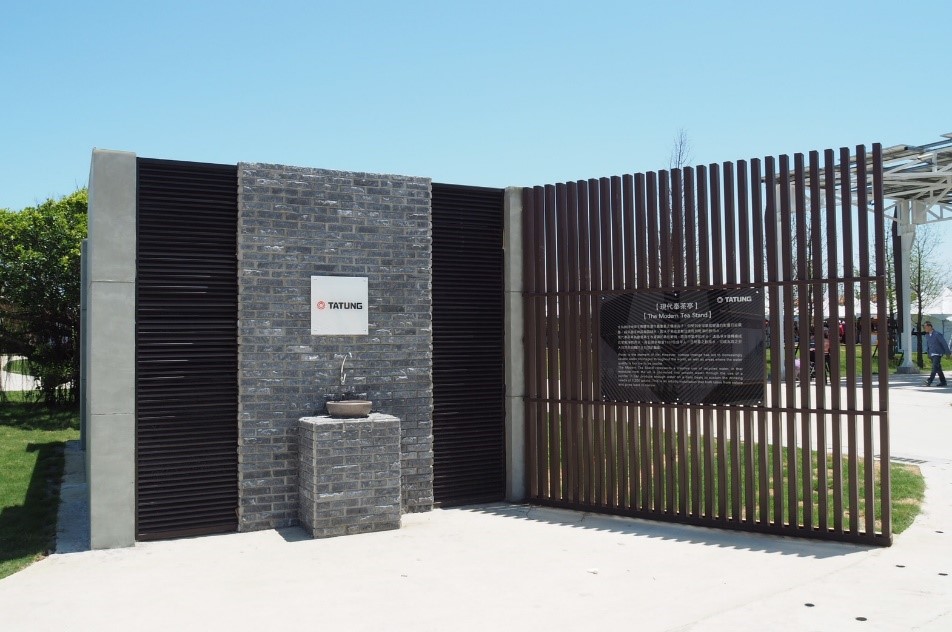
(A)Creating drinking water with technology
The Park uses technology to collect water in the air and then filter it by using three-level water purifier. This creates 2,400 liters of clean alkaline drinking water each day, which can be offered to 1,200 adults. Not only is it free of cost, but also this collected-from-the-nature water will also be given back to the nature.
Figure 12. The technology created water source – The Modern Tea Stand
(B)Applications of electric and driverless cars
The demonstration site provided the possibility to verify relevant technology and facilitated the cooperation between international AI companies and domestic automobile manufacturers with respect to the establishment of the self-driving AI mode. Not only can this mode plan the routes and evaluate road alignments even more precisely, but also relevant safety preventive measures are also applied in practice. During the TAE period, the brand new electric shuttle bus was also adopted and succeeded in transporting 308,458 passengers; and the self-driving electric car was used to demonstrate the guided tour for 667 times with 4,031 passengers. Technology transfer and cooperation will be taken place in the future in order to apply relevant technology in other electric cars and fields (ex. farm house and storage) for agricultural transportation.
Figure 13. Applications of self-driving driverless cars
IV.Results of Demonstration
1.Economic benefits
(A)Visitors:
he innovative agricultural values and other values created together with technology, life, ecology and environmental protection have attracted 3,394,147 visitors.
(B)Business opportunities:
According to the statistics, the average expense of each person during TAE is about NT$442.38. By multiplying this number with 3.39 million visitors, the total benefit will be about NT$1,499,668,200.
(C)Corporate investment:
During this demonstration, Taoyuan City has cooperated with 38 companies, having them sponsored exhibition and relevant services with a total value of over NT$50 million. Besides, over NT$50 millions of order were also created during the process of preparing and holding for TAE. In total, this demonstration has created about NT100 millions of agricultural value.
2.Low-carbon benefits
The Park’s first agricultural smart grids are located in 10 electricity generation facilities within the park, including two photovoltaic corridors, the weather station turbine and the green house roof top. In total, it has generated 127,970 kWh, which can be supplied to 427 households for one entire month. In overall, the generated electricity was sufficiently used by the entire Park.