In the 21st century, many countries around the world are investing important efforts to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in response to climate change, and Korea is one of those. In particular, in 2009 the Korean government decided to contribute on this climate issue by setting a 30% GHG emission reduction target by 2020. In order to achieve this ambitious goal, the Smart Grid technology has been identified as an effective solution.
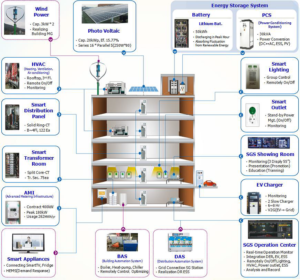
"Smart Grid Station" of Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) is an integrated regional-based control center for best-managing independent energy systems converged with information and communication technologies. The project widely embraced diverse areas of smart grids and renewable energy encompassing heating/cooling, photovoltaic, wind turbine, energy storage system, advanced meter infrastructure, and electric vehicle charger, while implementing technologies developed from the Jeju smart grid pilot project (2009-2013).
The project developed a hybrid power conversion system (PCS) and energy management system (EMS) in order to efficiently integrate systems and manage energy consumption in buildings. In the “Smart Grid Station,” each building is installed with an EMS that integrates various independent systems, such as renewable energy resources, energy storage, smart devices, heating and cooling devices, etc. The hybrid PCS successfully integrates the inverter that controls renewable energy sources and the power conversion system, which controls charging/discharging status of batteries while the EMS monitors and controls the Smart Grid Station system components.
In order to most efficiently manage a building’s energy consumption, the SGS has independently developed hybrid power conditioning system (PCS) and EMS. The main task of the hybrid PCS is to integrate the photovoltaics, wind and storage systems under the same control unit. The PCS converts the DC energy generated from renewable energy facilities to power the battery and provide AC electricity. It has eight different operation modes and receives orders from the EMS to operate accordingly. Hence, hybrid PCS has both an economic advantage and strong technological features. On the other hand, the EMS monitors and controls all the systems of the SGS components. The ESS charging/discharging algorithm that reflects load patterns also automatically optimizes energy usage, peak load, cooling/heating, etc. It has additional functions, such as energy source trading and load shedding during energy shortages.
The Smart Grid Station of KEPCO reduced indoor energy consumption by 10% of and reduced peak demand by 5%. By better enabling effective demand side management, peak demand reductions, and load shedding, the project reduces transmission and distribution costs, while stabilizing energy supply and demand. The Smart Grid Station project involved 39 different small and medium enterprises participating in the 2014 project and there are plans to expand the application of the Smart Grid Station to 75 KEPCO buildings in 2015.
Global Expansion of the concept
In 2016, KEPCO broke ground on a Smart Grid Station project in Dubai with Dubai Electricity and Water Authority.
Sources
Global Power Journal. DEWA And KEPCO Break Ground On Smart Grid Station. 24 May 2016
Global Smart Grid Federation. KEPCO Smart Grid Station Project. 2015 July 6.
International Smart Grid Action Network. 2015 ISGAN Award of Excellence. 2015