Future-generation Power Network Stabilization Technology Development for Utilization of Renewable Energy As the Major Power Source (STREAM Project)
In October 2020, the Extraordinary session of the Japanese Diet declared the goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, and in October 2021, the Sixth Strategic Energy Plan approved by the Cabinet indicated that the share of renewable energy would be around 36-38% in 2030.
The importance of expanding the introduction of renewable energy is increasingly being acknowledged. In order to expand the introduction of renewable energy, the Sixth Strategic Energy Plan follows the Fifth Strategic Energy Plan in “overcoming grid constraints” for “making renewable energy the main source of power”, with the expectation that this will be realized through research and development.
This STREAM project, based on the results obtained from the NEDO project called “Next-Generation Power Network Stabilization Technology Development for Large-Scale Integration of Renewable Energies”, aims to develop technologies to address new challenges like low inertia and short circuit capacity while comprehending the latest technological and policy trends, taking into consideration any possible technological or even institutional risks in the future power grid.
In addition, it will be verified that the results of the development are appropriately effective in small-scale power grids.
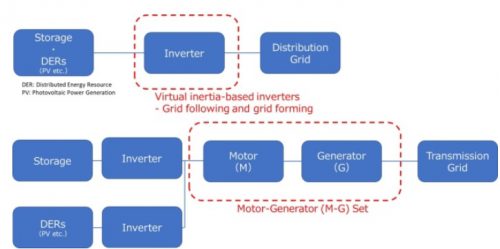
R&D Item: Development for the Practical Application of Inverters With Synthetic Inertia
NEDO will develop equipment that combines inertial functionality and standalone operation detection functionality as current control (grid following) inverters and voltage control (grid forming) inverters, which are mainly targeted at distribution systems. In addition, NEDO will consider solutions and develop the necessary functions for issues such as the smaller fault current generated by inverters compared to rotating generators, which may result in inadequate fault detection. NEDO will verify the stable operation of the developed inverters with sysnthetic inertia when multiple units are introduced in a small-scale grid. Furthermore, NEDO will acquire data necessary for reflection in the Grid-interconnection Code etc.
R&D Item : Development of Practical M-G Sets
NEDO will verify the development of M-G Sets connected to renewable energy and storage batteries to demonstrate behavior like conventional rotating generators even in the event of power system disturbance, contributing to the stability of the power system. Specifically, NEDO will verify that the renewable energy and storage batteries do not stop operating due to overvoltage and overcurrent on the system side of the motor (M side) of the M-G set in cases where the output of renewable energy decreases rapidly or when the charging and discharging of storage batteries are performed rapidly. In addition, by effectively utilizing storage batteries, NEDO will also verify grid stabilization control that is not available with existing synchronous generators, for example, the control to rapidly reduce power from storage batteries in the event of a ground fault on the backbone grid.
Project period: FY2022 to FY2026, budget: 3 billion yen (FY2023)
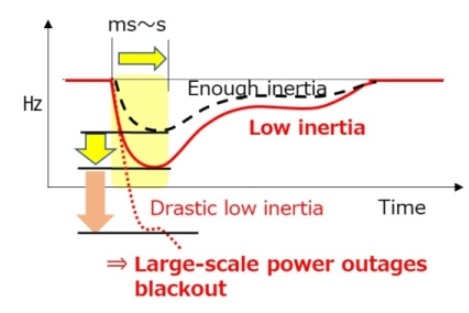
Impact of Low Inertia on Frequency Fluctuations (Concept)