Before the implementation of Bus Rapid Transit, the modal share of public transport in Nagoya was significantly lower than that of other cities in Japan, while that of the automobile was high. In 1979, 11.1% of total trips were made by buses, 11.6% by metro, 16.5% by heavy rail, and 56.2% by private car. Traffic congestion was severe especially during peak hours.
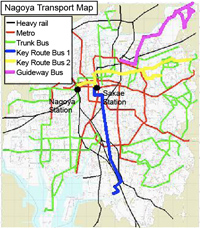
In order to increase the modal share of public transport and reduce traffic congestion, the Municipal Government of Nagoya developed a BRT system beginning in the early 1970s. They developed trunk bus systems, including “Guideway” buses, “Key Route” buses, and “Trunk” buses, along the major roads mot served by metro. The most well developed BRT systems are “Guideway” bus (opened in 2001) and “Key Route” buses (opened in 1982 and 1985). Also, other general buses provide feeder services connecting these main routes. As of this writing (2007), the total length of the existing 29 bus lanes is 90 km, most of which become exclusive buses lanes during peak hours, although they serve as mixed traffic lanes at other times. The average bus speed is 15 kph.
Raised Exclusive Guideway – Guideway Buses: The buses run on the raised exclusive guideway (busway) above the roads with a high speed of 30kph, automatically guided by electricity in the city center. In the suburbs, where traffic is less, they run on existing roads as do other buses. The total route is 11.9km, 6.8km of which is exclusive guideway.
Exclusive Bus Lane Only During Peak Hour – Key Route Bus: The system uses bus priority lanes that become exclusive bus lanes during peak hours (7:00–9:00, 17:00–19:00). The bus lane for Line 1 is located at each side of the road while that of Line 2 is at the center of the road. The interval between each bus stop is designed as 600m. The total length of each line is about 10km.
Public The Transport Development Project Focusing on Reduction of Congestion and Environmental Burden: The BRT project in Nagoya focuses on increasing public transport modal shares to reduce traffic congestion and environmental burdens rather than the financial profitability of the project. The Nagoya Transport Authority in the municipal government is the implementation body of most parts of BRT system and the whole metro system in Nagoya as well as one of the bus operation bodies and only one metro operating entity. Although the authority’s operation balance has been in deficit, the municipal government has been investing for their operation and implementation of new lines to make Nagoya a more public transport oriented city.
Public Transport System Consisting of Metro and the Bus Network: Unlike most other BRT systems in the world where BRT is the main intracity public transport system by itself, BRT in Nagoya is a part of a public transport system that consists of both metro and the bus network. Because bus lane development is much less expensive than metro construction, busways were developed in the 1970s–1980s along the major roads that were not served by metro. However, when in the 1990s it became clear that bus lanes were less competitive with private vehicles compared to metro, the Nagoya Transport Authority changed its policy on BRT to further develop metro and convert its bus system into a feeder system for metro, a policy that is still pursued.
BRT Development without Organizational Reform: Since there were only two major operating bodies for intracity buses in Nagoya, the Nagoya Transport Authority and Meitetsu Bus Corporation (a private company), when the BRT system was developed in the 1970s, organizational reform of bus operating bodies was not necessary for implementation of the BRT system in Nagoya. Therefore, even after bus lanes were installed, the existing two operating bodies continued bus operation along the same routes as before. Only for Guideway buses opened in 2001, a so-called third-sector (joint public private venture) company was newly funded because of the project’s low profitability.
Public Sector Investment Scheme for Financially Less Profitable Project – Third Sector Scheme: The Guideway Bus System was implemented and has been operated by a third-sector (joint public private venture) company, Nagoya Guideway Bus Corporation. In such a third sector scheme, the public sector is responsible for most of the initial investment and delegates operation to the third-sector company. In this project, the Nagoya Municipal Government plays the main role of the public sector. Of the total implementation cost of 37.5 billion yen, the public sector owed 32 billion yen while the third sector company owed 5.5 billion. This financial structure is applicable only to projects that are not financially profitable but bring other benefits such as reductions in traffic congestion and emissions.
Busways Located at the Center Lanes and Side Lanes: The bus lane of Key Route Bus Line 2 is located at the center of the road, while that of Line 1 is located on both sides of the road, since bridge piers of the urban expressway do not allow center lanes. Since center lanes enable bus operation without conflicts from cars turning at intersections, stopping on the route, or running ahead, operations along Line 2 are much faster and performance more on time compared to Line 1.
Traffic Regulation with Colored Lanes: To clarify the bus lanes and strengthen the traffic regulation effect, all lanes of Key Route Bus Line 2 and some parts of Line are colored orange-yellow. In addition, Line 2 has a monitoring system on the bus route, which enables warning announcements to private vehicles entering the bus lane.
ITS Operation Adjustment: Key Route Bus Line 2 has a total control system, consisting of one central processor, CRT, and intelligence gathering equipment on the route and buses, which enable operation adjustment depending on passenger demand.
Park and Ride System: At one of the terminuses of the Key Route Bus Line 2 route, a bus terminal, a cycle parking space, and a car park for “park and ride” were newly provided at the same time as opening of Line 2 to increase its usability.
Guideway Bus: The Guideway Bus has both general tires to run on the road and guiding equipment leading the vehicle on the guideway. This system enables the vehicles to run on an elevated guideway on the routes with high traffic demand and to travel on general roads in suburban areas with low traffic volumes.